Welcome to our exploration of geofencing for cars and trucks. In this blog, we'll delve into how this technology is transforming vehicle management and security. Our journey will cover various aspects, from enhancing fleet efficiency to bolstering security measures.
Whether you're a fleet manager or just curious about vehicle technology, this piece offers valuable insights. Stay tuned as we discover the potential of geofencing in the realm of vehicles and heavy-machinery.
Let's define what a geofence is before we dive deeper.
A geofence is essentially an invisible boundary, similar to a virtual fence, set around a physical location. It functions like a real fence by creating a clear boundary between that specific area and its surroundings. However, unlike a tangible fence, a geofence is also capable of detecting and reacting to movement within this virtual border, offering a blend of flexibility and precise surveillance.
What is Geofencing?
Geofencing is a location-based service that uses GPS, Wi-Fi, or cellular data to trigger an action when a mobile device or RFID tag enters or exits a virtual boundary set up around a geographical location. This virtual boundary, or geofence, can be customized to any shape or size, making it a versatile tool for various applications.
The technology allows for real-time monitoring and management of assets within these virtual perimeters. It’s particularly useful in sectors like transportation, security, and marketing, where location-specific strategies or security measures are crucial.
To put in simply, geofencing creates an invisible barrier that can be programmed to send alerts, trigger notifications, or initiate certain actions when crossed by a designated device. This makes it an essential tool for businesses and organizations that require precise location-based control and monitoring.
How Does a Geofence Work?
The technology behind a geofence is both innovative and straightforward. When a device (e.g., telematics device) enters or exits the geofenced area, it triggers a response. This is achieved through the use of GPS, Wi-Fi, or cellular data to accurately pinpoint the location of the device in relation to the predefined geofence.
Once the device crosses the geofence boundary, the system detects this movement and initiates a programmed action. This action can vary depending on the application – it could be a push notification sent to a smartphone, an alert to a monitoring system, or a signal to trigger other technological processes.
|
Step
|
Technology Involved
|
Process
|
Outcome
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Location Technology | Utilizes GPS, Wi-Fi, or cellular data | Identifies the device's location |
| 2 | Geofence Software | Sets the geographical parameters of the geofence | Defines the virtual boundary |
| 3 | Device Crossing | Detects when a device enters or exits the geofence | Triggers a predefined response |
| 4 | Communication Network | Replays information between the device and system | Ensures timely and accurate action |
Key to this process is the software that defines the geofence. This software not only sets the geographical parameters of the geofence but also dictates the type of response that will be triggered upon entry or exit. The software is typically part of a larger application or system that interprets the geofence crossings and acts accordingly.
Another crucial element is the communication network, which relays the information between the device and the geofencing system. This network ensures that the response is timely and accurate, a critical factor in scenarios where immediate action is required, such as in security or safety-related applications.
In What Ways Can Geofencing Be Used?
The need for geofencing varies significantly from one user to another, and its applications are as diverse as they are valuable. Especially in fleet management, telematics, and personal vehicle use, geofencing solutions and platforms offer essential benefits.
Fleet Management: Geofencing solutions are crucial in the world of fleet management. They provide real-time monitoring and ensure that vehicles follow to prearranged routes and areas. This capability is vital for streamlining logistics, guaranteeing timely deliveries, and boosting operational efficiency. If a vehicle strays from its intended path, the geofencing platform can immediately alert fleet managers, aiding in the prevention of unauthorized use or deviations that might lead to delays and extra costs.
Telematics Solutions: In telematics solutions, geofencing platforms are needed for data collection on vehicle usage, driver behavior, and route efficiency. This data, gathered when vehicles enter or exit a geofence, enables companies to analyze fleet performance, refine routes, and enhance the overall efficiency of their fleet. Such insights are also beneficial for predictive maintenance strategies, reducing the risk of vehicle failures.
Geofencing in Cars: Geofencing solutions extend their utility to personal vehicles, offering advanced security features. For instance, if a car moves outside a predetermined geofence, the owner receives an alert, an essential tool in theft prevention. For families, these geofencing platforms can track the whereabouts of young or inexperienced drivers, providing an additional layer of safety.
In each scenario, geofencing platforms and solutions provide unparalleled control and insight. By establishing geographic boundaries and receiving instant alerts when these are crossed, users can more effectively manage vehicles, ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with both regulatory and internal policies.

How AutoPi Cloud Makes Fleet Management Easier
As a business owner, you're juggling a lot. The last thing you want is to be stuck at your desk all day, trying to keep track of every vehicle. That’s where AutoPi Cloud comes in. With our geofencing feature, you can set virtual boundaries for your vehicles and get real-time updates when they enter or leave key areas.
Whether it’s making sure deliveries stay on track or keeping vehicles where they’re supposed to be, you’ll know exactly what’s going on—without having to constantly check your phone. It’s all about giving you peace of mind and letting you focus on what matters most.
The Technical Aspects of Geofencing Technology
The technical aspects of geofencing technology reveals a interplay networking of various components that make geofencing a robust and versatile tool.
Location Sensing Technology: Central to geofencing is the location-sensing technology. This involves the use of Global Positioning System (GPS), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Wi-Fi, or cellular data to accurately determine the position of a device relative to the geofenced area. GPS offers widespread outdoor coverage, while RFID, Wi-Fi, and cellular data are more suitable for precise indoor tracking.
Geofence Configuration Software: The creation and management of geofences are handled by specialized software. This software enables the definition of geofence parameters such as size, shape, and location. Advanced platforms offer customizable options like time-based geofences or geofences that adjust in size and location depending on various factors.
Trigger Mechanisms and Responses: The heart of geofencing technology lies in its trigger mechanisms and the corresponding responses. These triggers are activated when a device enters, exits, or dwells in a geofenced area. The system can be programmed to send notifications, record data, or initiate other actions like locking doors or triggering alarms.
Integration with Other Systems: Modern geofencing technology often integrates seamlessly with other systems and applications. This integration allows for enhanced functionality, such as combining geofencing with telematics systems in vehicles for advanced fleet management.
Data Analytics and Reporting: Geofencing technology is also paired with data analytics and reporting tools. These tools analyze the data collected from geofence crossings to provide insights into patterns and trends, which can be crucial for optimizing operational processes, enhancing security protocols, or developing targeted marketing strategies.
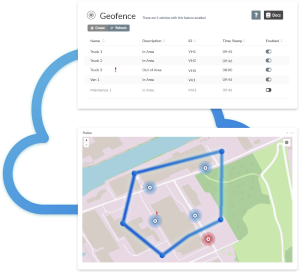
How Do I Create a Geofence?
Creating a geofence with the AutoPi Device and AutoPi Cloud is a straightforward process, thanks to the pre-built technology by professional developers. Here's a step-by-step guide to setting up your own geofence:
-
Step 1: Equip Your Vehicle with AutoPi TMU Device
To start, ensure that your vehicle is equipped with an AutoPi device and that you have access to AutoPi Cloud. This setup is essential for geofencing. Check our Getting Started Guide.
-
Step 2: Access the Geofence Function
Simply log in to your AutoPi Cloud account. The geofence feature is readily available as a default function for all users, allowing you to start creating your geofences right away without the need for any additional setup.
-
Step 3: Choose Your Geofence Type
AutoPi Cloud offers two ways to create a geofence:
— Circle-Based Geofences: Use the circle zone-import tool in AutoPi Cloud. Click on the map to set the center point and adjust the size to create your desired zone. This is ideal for scenarios like monitoring when vehicles enter an area around a specific location, such as a warehouse.
— Polygon-Based Geofences: For more specific area requirements, you can create a geofence using corners. Click on the map to outline the corners of your desired zone. This method is useful for tracking entry and departure times from specific locations like job sites.
-
Step 4: Set Up Conditional Triggers
Geofences are not just digital shapes on a map; their true power lies in the conditional triggers that can be set up in AutoPi Cloud. You can design custom triggers to receive notifications for specific events, such as when a truck enters the predefined geofence zone.
-
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust as Needed
Once your geofence is set up, you can monitor the activities. AutoPi Cloud allows you to view geofences and adjust them as needed, ensuring you get the most out of your geofencing setup.
Creating geofences with the AutoPi system is a blend of simplicity and flexibility, allowing you to efficiently manage and monitor vehicle movements in relation to your specific business or personal needs.